Understanding the UK Government’s AI Assurance Regime and Why It Matters
- sas8801
- Jan 18, 2025
- 5 min read
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming industries at an unprecedented pace, revolutionising areas such as healthcare, finance, transport, and entertainment. However, alongside its immense potential, AI has brought significant challenges, raising concerns about bias, privacy violations, security risks, unintended consequences, and accountability gaps.
For example, biased algorithms can exacerbate inequality, opaque decision-making processes hinder accountability, and the misuse of AI in areas like surveillance or disinformation poses profound ethical dilemmas. Furthermore, the complexity of AI systems makes it difficult for organisations to ensure compliance with ethical and technical standards, while a lack of clear regulation creates uncertainty for businesses and investors.
To address these pressing issues, the UK government is developing an AI assurance regime—a comprehensive framework designed to evaluate, certify, and build trust in AI systems. This initiative is a cornerstone of the UK’s National AI Strategy and aims to ensure that AI technologies operate safely, ethically, and in alignment with public interest.
This blog post explores the UK’s AI assurance regime, its key components, and why it is vital for mitigating risks, fostering trust, and securing the UK’s position as a global leader in responsible AI innovation.

What is the AI Assurance Regime?
The AI assurance regime is an evolving ecosystem of standards, certifications, and governance frameworks created to assess and certify the reliability, safety, and ethical integrity of AI systems. It provides a structured approach to evaluating AI technologies, enabling developers, businesses, and end users to identify and mitigate risks while fostering innovation.
This initiative builds on the UK’s ambition to become a world leader in ethical AI governance, as outlined in its National AI Strategy. By prioritising transparency, accountability, and inclusivity, the regime aims to create a robust foundation for safe and responsible AI adoption.
Key Components of the UK AI Assurance Regime
1. Development of Standards
The regime aligns with global efforts to establish technical and ethical standards for AI, collaborating with international organisations like ISO and IEEE. By influencing these standards, the UK ensures its framework is both relevant and globally competitive
.
2. Independent Certification and Auditing
AI systems will undergo independent assessments to verify their compliance with established standards. Certifications provide businesses with third-party validation, demonstrating their commitment to ethical AI practices and instilling confidence among users and investors.
3. Transparency and Explainability
A critical focus of the regime is ensuring AI systems are transparent and their decision-making processes are understandable. This is essential for building trust, particularly in sectors where AI decisions have significant consequences, such as healthcare, law enforcement, and finance.
4. Sector-Specific Guidance
Recognising that the risks and opportunities of AI vary across industries, the regime provides tailored guidance to address the unique challenges of each sector, ensuring effective and practical implementation of assurance measures.
5. Stakeholder Collaboration
The government is engaging with businesses, academia, and civil society to co-create the assurance framework. This inclusive approach ensures that diverse perspectives are considered, fostering widespread adoption and legitimacy.
Why is the AI Assurance Regime Important?

1. Building Public Trust
AI systems are increasingly influencing critical aspects of daily life, from medical diagnoses to employment decisions. Without robust assurance mechanisms, public confidence in these technologies could erode, hindering adoption and innovation. The AI assurance regime provides the tools and processes to demonstrate that AI systems are safe, fair, and aligned with societal values.
2. Mitigating Risks to Citizens and Businesses
AI technologies carry inherent risks, such as algorithmic bias, misuse, and vulnerabilities to cyberattacks. For example, biased recruitment tools can perpetuate inequality, while insecure AI systems are susceptible to exploitation. The assurance regime helps mitigate these risks, protecting individuals and businesses from harm.
3. Encouraging Ethical Innovation
By embedding ethics and safety into the design and deployment of AI systems, the regime promotes innovation that aligns with societal goals. This ensures that AI technologies drive progress without compromising values such as fairness, accountability, and human dignity.
4. Strengthening the UK’s Global Competitiveness
As AI becomes a cornerstone of global economic growth, countries that lead in ethical AI governance will gain a competitive edge. By proactively developing an assurance regime, the UK positions itself as a global leader in responsible AI, attracting investment and fostering innovation in alignment with international standards.
5. Preparing for Future Regulation
The AI assurance regime lays the groundwork for future regulation, ensuring UK businesses are prepared for emerging compliance requirements both domestically and internationally. This proactive approach reduces uncertainty, creating a stable environment for innovation and investment.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
While the UK’s AI assurance regime represents a significant step forward, it is not without challenges. Establishing universally accepted standards, ensuring effective enforcement, and addressing the rapid pace of technological development will require ongoing collaboration and adaptability. Additionally, fostering global cooperation on AI governance is essential to ensure harmonisation across borders.
The success of the regime will depend on its ability to balance innovation with risk mitigation, enabling the UK to lead in shaping an ethical and inclusive AI future.
Key Ecosystem Players and Their Roles
The UK’s AI assurance regime relies on a diverse ecosystem of stakeholders working collaboratively to ensure AI systems are safe, ethical, and effective. Each player in this ecosystem has a critical role in shaping, implementing, and maintaining the regime. Below is an overview of the key players and their responsibilities:
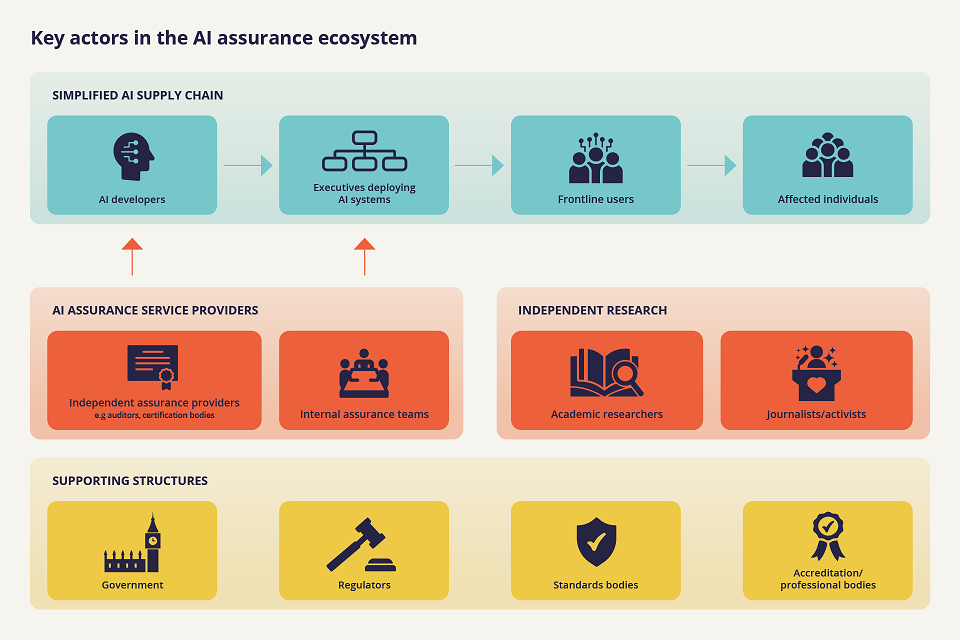
1. Government and Regulators
• Role: Policymaking, standard-setting, and enforcement. Examples: The Department for Science, Innovation and Technology (DSIT) and the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) are key governmental bodies driving the UK’s AI policy and privacy regulations.
2. Standards Bodies
• Role: Developing technical and ethical benchmarks. Examples: The British Standards Institution (BSI) is actively involved in AI-related standardisation efforts in the UK.
3. Certification and Audit Organisations
• Role: Independent evaluation and verification of AI systems. Examples: Third-party certifiers such as those accredited by UKAS (United Kingdom Accreditation Service).
4. Academic and Research Institutions
• Role: Providing foundational knowledge and thought leadership. Examples: Institutions like the Alan Turing Institute play a central role in advancing AI ethics and technical research.
5. AI Developers and Organisations
• Role: Designing and deploying AI systems responsibly. Examples: Leading AI companies and start-ups developing AI solutions across sectors such as healthcare, finance, and transportation.
6. Industry and Trade Associations
• Role: Advocating for industry interests and promoting best practices. Examples: TechUK, a leading trade association, represents the UK’s tech sector in AI governance discussions.
7. Civil Society and Advocacy Groups
• Role: Representing public interest and promoting accountability. Examples: Organisations like the Ada Lovelace Institute focus on the ethical implications of AI in society.
8. Investors and Financial Institutions
• Role: Funding responsible AI innovation. Examples: Venture capital firms and banks funding AI-driven start-ups and projects.
9. End Users and Consumers
• Role: Driving demand for trustworthy AI.
Collaboration for Success
The UK’s AI assurance regime depends on collaboration between these players to create a cohesive, effective, and future-proof ecosystem. By combining the expertise and perspectives of each stakeholder, the regime can ensure that AI technologies are not only innovative but also safe, ethical, and beneficial to society. This collective effort will solidify the UK’s leadership in responsible AI development and governance.
Conclusion
The UK government’s AI assurance regime is a bold and necessary initiative to address the ethical, safety, and accountability challenges posed by AI. By creating a clear and robust framework for evaluating AI technologies, the regime fosters trust, reduces risks, and positions the UK as a global leader in responsible AI governance.
As this initiative continues to develop, it offers an opportunity for businesses, policymakers, and society to work together in building a future where AI serves the greater good—empowering innovation while safeguarding public interest.
The UK’s commitment to this vision sets an inspiring example for how nations can lead in the age of AI, ensuring that this transformative technology benefits everyone.




Comments